In vivo NeoLNP™ RNA Systemic Transfection Kit
| Catalog Number | Product Specification | Product Composition | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transfection Reagent | Buffer | RNA Positive Control | ||
| SDR8002 | SDR8002-0.3mL | 0.3mL × 1 vial | 8mL × 1 vial | 10µg × 1 vial |
| SDR8002-0.5mL | 0.5mL × 1 vial | 8mL × 2 vials | 10µg × 1 vial | |
| SDR8002-1.0mL | 1.0mL × 1 vial | 8mL × 3 vials | 10µg × 1 vial | |
For placing an order or more information about the products, please contact us by sending an email to service@scindypharm.com or calling +86 (512) 8886-5668.
Scindy Pharmaceutical’s next-generation in vivo lipid nanoparticle technology integrates cutting-edge targeted delivery strategies while building on traditional delivery methods. Our in vivo NeoLNP™ technology enhances the accuracy and efficiency of RNA delivery through innovative lipid formulations and personalized targeting ligand designs.
The In vivo NeoLNP™ RNA Systemic Transfection Kit (SDR8002) is a versatile in vivo RNA delivery solution. Utilizing innovative ready-to-use LNP in vivo delivery technology, SDR8002 supports transient encapsulation of siRNA, miRNA, sgRNA, mRNA, and other RNA types, enabling systemic RNA transfection via multiple administration routes, providing a more efficient and rapid solution for RNA research and clinical translation.
![]() Compatible with Multiple RNA Types:
Compatible with Multiple RNA Types:
Suitable for delivering siRNA, gRNA, mRNA, circRNA, and more.
![]() Flexible Administration Routes for Diverse Research Needs:
Flexible Administration Routes for Diverse Research Needs:
SDR8002 supports multiple administration routes, exhibiting distinct tissue distribution profiles to meet needs for vaccines, protein replacement, and gene regulation.
![]() Intravenous Injection (IV) - Targeting Liver/Spleen
Intravenous Injection (IV) - Targeting Liver/Spleen
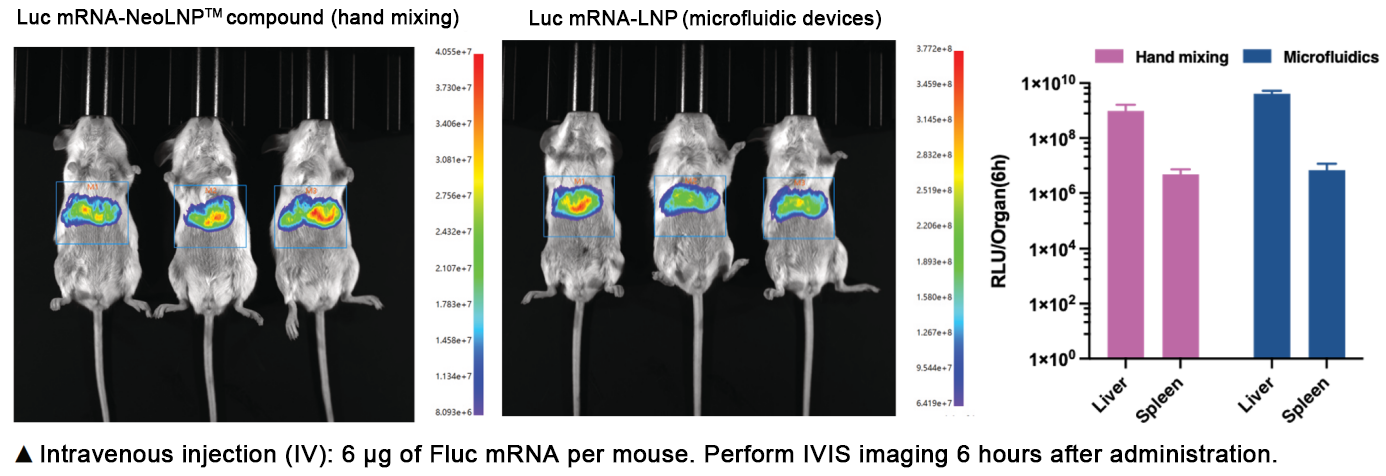
After IV injection of Fluc mRNA-NeoLNP™ complex, fluorescence protein is primarily expressed in the liver, followed by the spleen, with fluorescence intensity comparable to microfluidically encapsulated mRNA-LNP. SDR8002’s tissue distribution makes it an ideal carrier for RNA therapies targeting metabolic or genetic liver diseases.
![]() Intramuscular Injection (IM) - Vaccines:
Intramuscular Injection (IM) - Vaccines:

Six hours after IM injection of Fluc mRNA-NeoLNP™ complex, fluorescence protein expression is concentrated at the injection site, liver, and spleen, consistent with the tissue distribution of approved mRNA-LNP vaccines. SDR8002 is an ideal choice for vaccine development.
![]() Intraperitoneal Injection (IP) - Multi-Organ/Tissue RNA Delivery:
Intraperitoneal Injection (IP) - Multi-Organ/Tissue RNA Delivery:
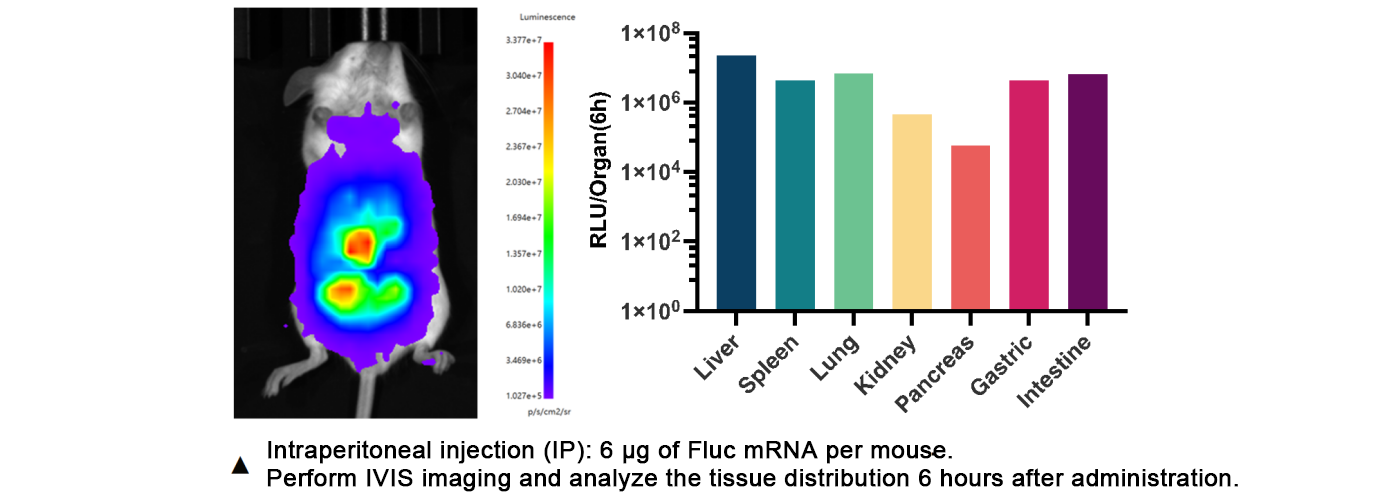
Six hours after IP injection of Fluc mRNA-NeoLNP™ complex, significant fluorescence signals are observed in the liver, spleen, lungs, kidneys, stomach, and intestines, demonstrating SDR8002’s capability for efficient, widespread systemic RNA delivery.
![]() Higher Safety:
Higher Safety:
● Uses biodegradable lipid materials with excellent biocompatibility.
● Free of organic solvents like ethanol, reducing injection site irritation.
● Enables effective delivery to target tissues or organs via different administration routes, ensuring reliable and effective treatment.
![]() Why Choose in vivo NeoLNP™ NeoLNP™ Transfection Kit?
Why Choose in vivo NeoLNP™ NeoLNP™ Transfection Kit?
● Efficient: Maintains stable high transfection levels regardless of injection method.
● Flexible: Customizable for systemic or localized RNA delivery based on research goals.
● User-Friendly: Optimized delivery solutions enable rapid, efficient RNA encapsulation, simplifying experiments.
With the in vivo NeoLNP™ Transfection Kit, researchers can flexibly utilize multiple delivery routes to achieve precise RNA delivery, meeting unique research needs. From broad systemic applications to highly specific organ-targeted delivery, this kit is a powerful tool for cutting-edge RNA research.
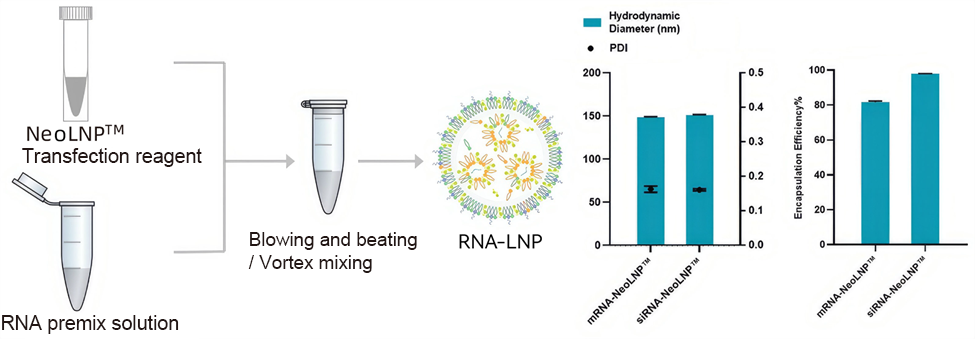
Ready-to-Use LNP In Vivo Delivery Technology
The in vivo NeoLNP™ Kit stands out for its rapid and efficient RNA encapsulation capabilities. Compared to traditional methods, it requires no complex equipment, achieving efficient encapsulation through simple mixing with RNA solutions, significantly reducing preparation time. This innovation enhances RNA stability and ensures efficient transfection, offering a new transfection experience compared to traditional liposome-based nucleic acid adsorption methods.
- Documents & Downloads





 Product Manual
Product Manual

 Optimization Guide
Optimization Guide
 Cell Transfection Cases
Cell Transfection Cases
 Product Poster
Product Poster
